#ANALYTICS IN INSURANCE SECTOR
In insurance sector, analytics can help a company create comprehensive roadmap for managing the entire lifecycle of a customer, from acquisition to lapse or maturity. Analytics can also help an insurer gain a company-wide view of a customer to gather insights and identify opportunities across all their business lines.
Most people agree that it is quite challenging to satisfy the different needs of external stakeholders in insurance sector just like any other company using an application for corporate reporting. Companies have started adopting to products like Oracle Hyperion Financial Close Suite and HFM for Insurance Quantitative Management and Reporting purposes.
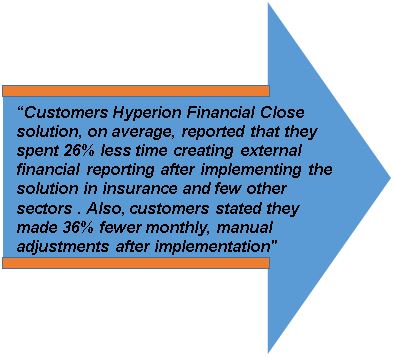
"Customers using Hyperion Financial Close solution, on average, reported that they spent 26% less time creating external financial reporting after implementing the solution in insurance sector. Also, customers stated they made 36% fewer monthly, manual adjustments after implementation".
We at Nomenclature can help you with the connected reporting solution that will help your company in responding to rising stakeholder demands and complexity in reporting. To list a few we serve and provide services in the following insurance categories
How is BI used in Insurance Sector ?
To manage through volatile times in a highly competitive market, insurance companies need a single view of the enterprise. That view must be flexible enough to connect with multiple policy administration and claims systems, extract data from those systems, and transform it into meaningful information. Operational, regulatory, and financial data must be completely transparent as business requirements change. Business intelligence (BI) can deliver the information that managers need to make critical decisions, and many are hungry for the value that added insight would deliver; yet they are cautious about projects that could take years to implement and returns that are difficult to predict.
One way to alleviate these concerns and build a strong business case for BI is to use both quantitative and qualitative metrics to evaluate the total potential return to the business. For most companies, the return generated by a BI implementation extends well beyond traditional cost-savings analysis to encompass far-reaching benefits, such as:
Client Implementation Story for a Insurance client :
Client Background: Major Insurance Provider
Client Business Need: Client wanted to automate data loading process for their EPMA Budgeting system.The various sources included Oracle GL, PeopleSoft HR, text files, and MS Excel files.
The Solution: We utilized ODI, Oracle Relational database, and FDMEE to create a comprehensive automated solution to extract, transform, and load data to the target EPMA application that was used for Budgeting and Forecasting.We utilized ODI packages to run data interfaces in a predefined manner. Data packages were scheduled to run from ODI agent and sent email notifications along with the data and error logs to the appropriate group. We also created a process to load finalized budget back to the GL through FDMEE.
Benefits:
Contact us at info@nomenclaturecorp.com if you suffer from any of the following
